
Introduction
Yemen (official name: Republic Of Yemen ) is a country located on the southwest corner of the Arabian Peninsula. Yemen shares most of its northern borders with the KSA. It is bordered by the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea from south, by the Red Sea from west and by Oman from east. Yemen has a land area of 527,968 km2. This includes several islands such as Kamaran and Hanish islands in the Red Sea, and Socotra and Bi’r Ali in the Arabian Sea. Sana’a is the capital. It is located in the western part of the country, on the foot of the western Jabal Nuqm, which is 7200ft (2200m) high above sea level. Over many centuries, Sana’a is considered an economic, political, and religious main center for the Yemeni heights, noting that its name means “the fortified place.”
Yemen’s history, culture, economy, and inhabitants were influenced by the strategic location of this country. The Red Sea southern entry is an ancient and modern trade crossroads for the whole world. The powers that earlier occupied the nowadays Yemen monopolized the supply of crucial products such as frankincense and myrrh.
Due to its fertile land and trade prosperity, Yemen was home to several ancient kingdoms. Later on, Yemen was the first place to grow coffee for trade purposes, before coffee plants were spread to other parts of the world.
In May 1990, the Republic of Yemen was established when the Arab Republic of Yemen (Northern Yemen) merged with the People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen (Southern Yemen). According to the Yemeni Unification Agreement, Sana’a (Capital of Northern Yemen) was declared the political capital of Yemen, while Aden (Capital of Southern Yemen) was declared the economic capital of Yemen.
Both Yemens (Southern and Northern) witnessed remarkably different histories. While northern Yemen hadn’t ever fallen under European colonization, southern Yemen was a part of the British Empire between 1839 and 1967. The republic’s present borders are mostly the result of foreign political agendas, and the doings of Britain, the Ottoman Empire, and the KSA.
Yemen suffered from chronic corruption and economic difficulties after the unification. Religious, tribal, and geographical divisions played a vital role in Yemeni politics, something that enhanced the occurrence of violence from time to time.
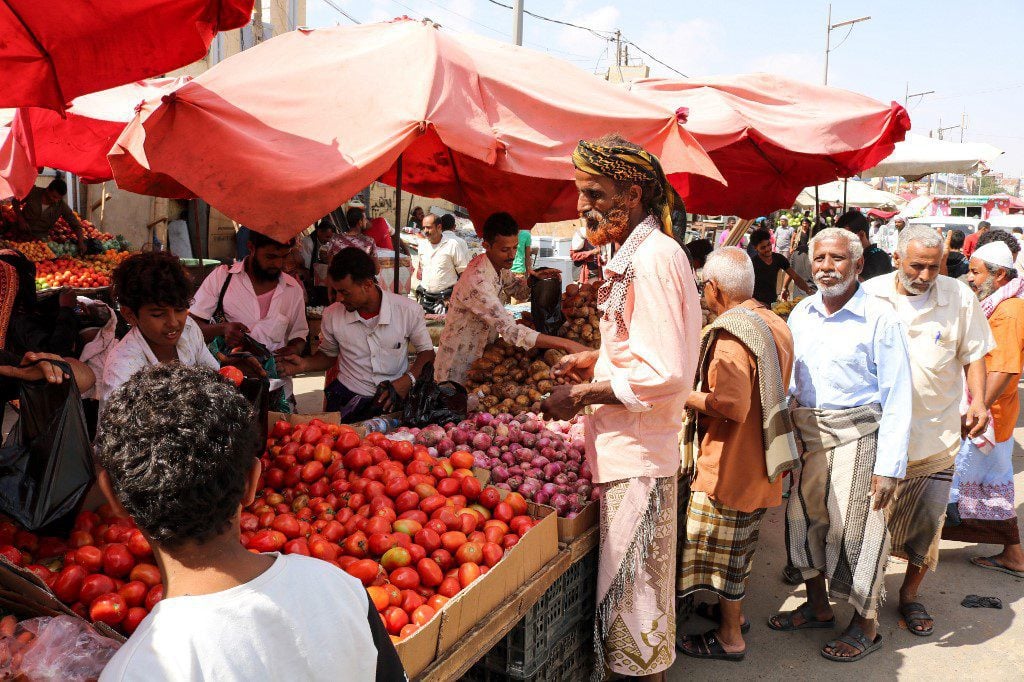
The Yemeni population is estimated at 30.49 million according to 2021 UN estimates. Arabs comprise the majority of the population, while some inhabitants have African, South Asian, and European origins.
Arabic is the official language of the country. Socotra language is widely used in Socotra Island and its archipelagos.
Islam is the official religion, as Muslims comprise about 99.1% of the total population (it is estimated that 65% are Sunni, and 35% and Shiite) according to 2020 estimates. The remaining include Jews, Baha’is, Hindus, and Christians, of which many are refugees or temporary foreign residents.
The Yemeni Riyal is the official currency of the country. Natural resources include oil, fish, rock salt, marble, and small deposits of coal, gold, lead, nickel, and copper; in addition to the fertile soil in the west.
In terms of military issues, Yemen is ranked 74th out of 145 countries included in the 2023 Global Firepower Index report..
Yemen ranks 169th out of 180 countries included in the 2022 World Press Freedom Index made by Reporters without Borders. The reason behind this low ranking might be attributed to the political division in the country between the Houthis in Sana’a and the government of President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi in Aden. The media environment became increasingly hostile towards press freedoms after the Houthis’ uprising against the Yemeni government in 2014, and air warfare or the KSA on the pro-Houthis targets.
The list of the Yemeni prominent faces includes the producer and director Khadija Al-Salami, the Leader of the Houthis Abdul-Malik Badr al-Din al-Houthi and the president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.
Camel Jumping is one of the traditional sports in Yemen. A player has to jump over a line of camels, and the winner is the one who can jump over the most camels. Over time, Yemenis fell in love with football, and it became the most popular sport in the country. This sport is managed by the Yemen Football Association. Yemen has not won any tournament, though it hosted the Arabian Gulf Cup in 2010.
Due to his exceptional skills, the forward of Al-Ahli Sanaa club Ali al-Nono was selected as the best Yemeni footballer. Unified Yemen didn’t participate in the Summer Olympics until 1992. However, Yemen has not been able so far to win a medal.
Most of Yemen is located in the region separating between two main types of winds; the usual north wind (from the Mediterranean basin) and the southwest seasonal wind. Winter is dominated by north wind, while the southwest seasonal wind brings the main rains in summer. The marginal southern regions of the Gulf of Aden are excluded from this pattern in the central mountains and have a remarkable tropical climate.
The country can be divided into 5 main regions: the coastal plain extending from north to south which is known as Tihamah; the western highlands; the central mountains (Yemen highlands); eastern highlands; and the eastern and northeastern desert areas. The coastal plain’s width ranges from 5 miles (8 km) to 40 miles (65 km).
The list of most popular tourist attractions includes Bab al-Yemen in the historic city of Sana’a, Dar Alhajar palace, baths of Hadhramaut, and the Golden Coast in Aden.
Driving vehicles is right sided, similar to the rest of the countries in the Middle East and North Africa. Time range for Yemen is (GMT+3). The international calling code is +967.





















