Introduction
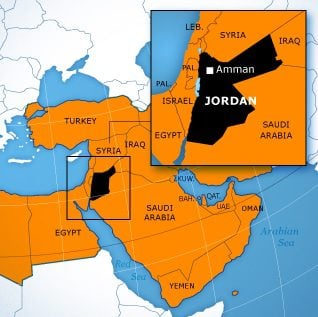
Jordan (officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan) is an Arab country in Southwest Asia, in the rocky desert of the northern Arabian Peninsula.
Jordan is bounded to the north by Syria, to the east by Iraq, to the southeast and south by Saudi Arabia, and to the west by Israel and the Palestinian territories (West Bank). Jordan has 16 miles (26 km) of coastline on the Gulf of Aqaba in the southwest, where Al Aqabah, its only port, is located.
Amman is the capital and largest city in the country. The name of the city is derived from the name of the Ammonites who made it their capital at the 13th century BC.
During the Roman era, Amman was given the name of Philadelphia which is derived from the name of its conqueror Ptolemy II Philadelphus. Nowadays, it serves as one of the region’s principal commercial and transportation centers. In addition, it is one of the Arab world’s major cultural capitals.
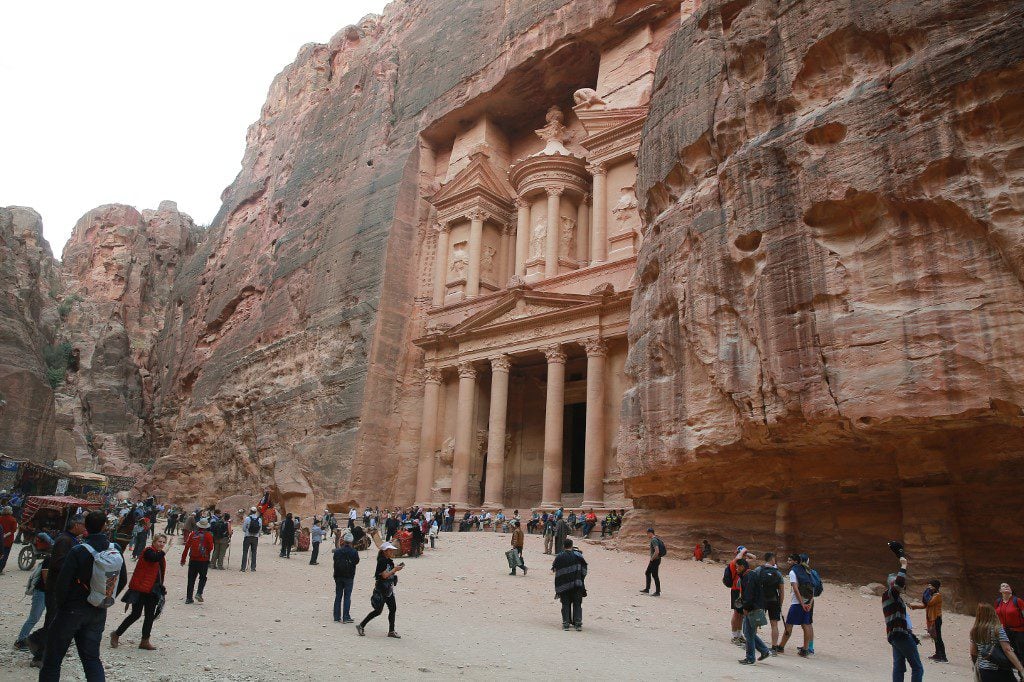
Jordan is a young state that occupies an ancient land, one that bears the traces of many civilizations. Separated from ancient Palestine by the Jordan River, this country played a prominent role in biblical history. The ancient biblical kingdoms of Moab, Gilead, and Edom lie within its borders, as does the famed red stone city of Petra, the capital of the Nabatean kingdom and of the Roman province of Arabia Petraea.
Jordan was part of the Ottoman Empire until 1918. Later, this country has been governed by a British mandate until gaining independence in 1946. Jordan is among the most politically liberal countries in the Arab world.
Although it shares in the troubles affecting the region, its rulers have expressed a commitment to maintaining peace and stability.
The country’s population is estimated at 10.27 million in 2021. Arabic is the official language. However, English is widely understood among the upper and middle classes.
Islam is the official religion of the kingdom. 97.2% of the population are Muslims (predominantly Sunni). Christians are estimated at 2.2% (majority Greek Orthodox, but some Roman Catholics, Coptic Orthodox, Armenian Orthodox, and Protestant denominations). Buddhist are estimated at 0.4% of the population, while Hindus and also Jews are 0.1%
Natural resources include phosphates, potash, and shale oil.
In military terms, Jordan is ranked 81 out of 145 among the countries included in the 2023 Global Firepower Report.
The modern media environment in Jordan is largely influenced by the government. It is not conducive to freedom of expression. The country was also ranked 120 on the 2022 World Press Freedom index of Reporters Without Borders.
According to one survey, 82 percent of Jordanians consumed news primarily via television. However, with a satellite penetration rate of over 90 percent. The majority of viewers opt for pan-Arab channels such as al-Jazeera, al-Arabiya, MBC, and LBC.
In 2007, Jordan became the first Arab country to pass a freedom of information law. The growth of internet access and use in the country since its introduction in 1995 has allowed for a greater degree of online independence and criticism.
However, cybercrime legislation is enforced to ensure that only moderate criticism is tolerated by King Abdullah across the media. The most popular domestic publications include Al-Rai newspaper, Ad-Dostour and Al-Ghad independent newspaper.
The list of prominent Faces includes the diplomat and reformer Marwan Muasher and Prince Zeid bin Raad al-Hussein.
In general, Jordan is one of the Arab countries paying great attention to youth and sports in Asia. This might be seen in many sports complexes and cities made especially for young people.
This has positively affected Jordan’s participation in many Arab, regional, and international championships, especially at the level of football and basketball.
Football is the most popular game in Jordan. The Jordanian national team started its international venue in the qualifications of Mexico’s 1986 World Cup. Since then, the team has maintained its presence in this venue. His best participation in the 2014 World Cup qualifications is the best ever. At that time, the national team succeeded in advancing toward the last step of the qualifiers against Uruguay in the FC-CONMEBOL play-off.
On the continental level, the Jordanian national team qualified for the Asian Cup on four occasions in 2004, 2011, 2015, and 2019. The national team participated once in the Youth World Cup. That was in the U-20 World Cup Championship in Canada in 2007.
The Climate of Jordan is mostly an arid desert. The western part of the country has a rainy season between November and April.
Jordan has three major physiographic regions (from east to west): the desert, the uplands east of the Jordan River, and the Jordan Valley (the northwest portion of the great East African Rift System).
The desert region is mostly within the Syrian Desert —an extension of the Arabian Desert—and occupies the eastern and southern parts of the country, comprising more than four-fifths of its territory. The desert’s northern part is composed of volcanic lava and basalt, and its southern part of outcrops of sandstone and granite.
The landscape is much eroded, primarily by wind. The uplands east of the Jordan River, an escarpment overlooking the rift valley, have an average elevation of 2,000–3,000 feet (600–900 meters) and rise to about 5,755 feet (1,754 meters) at Mount Ramm, Jordan’s highest point, in the south.
Outcrops of sandstone, chalk, limestone, and flint extend to the extreme south, where igneous rocks predominate. The Jordan Valley drops to about 1,410 feet (430 meters) below sea level at the Dead Sea, the lowest natural point on Earth’s surface.
The most important tourist attractions in Jordan include Petra, the Roman amphitheater in Jerash, and the Dead Sea which is rich in mineral salts.
Similar to the rest of the countries in the Middle East and North Africa, driving vehicles is right-sided.
Jordan’s time zone is (GMT +3) in summer and (GMT +2) in winter.
The international calling code is +962.